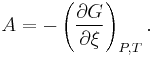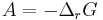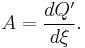Chemical affinity
In chemical physics and physical chemistry, chemical affinity is the electronic property by which dissimilar chemical species are capable of forming chemical compounds.[1] Chemical affinity can also refer to the tendency of an atom or compound to combine by chemical reaction with atoms or compounds of unlike composition.
According to chemistry historian Henry Leicester, the influential 1923 textbook Thermodynamics and the Free Energy of Chemical Reactions by Gilbert N. Lewis and Merle Randall led to the replacement of the term "affinity" by the term "free energy" in much of the English-speaking world.
Contents |
Modern conceptions
In modern terms, we relate affinity to the phenomenon whereby certain atoms or molecules have the tendency to aggregate or bond. For example, in the 1919 book Chemistry of Human Life physician George W. Carey states that, "Health depends on a proper amount of iron phosphate Fe3(PO4)2 in the blood, for the molecules of this salt have chemical affinity for oxygen and carry it to all parts of the organism." In this antiquated context, chemical affinity is sometimes found synonymous with the term "magnetic attraction". Many writings, up until about 1925, also refer to a "law of chemical affinity".
Ilya Prigogine summarized the concept of affinity, saying,
| “ | All chemical reactions drive the system to a state of equilibrium in which the affinities of the reactions vanish. | ” |
Thermodynamics
The present IUPAC definition is that affinity A is the negative partial derivative of Gibbs free energy G with respect to extent of reaction ξ at constant pressure and temperature.[2] That is,
It follows that affinity is positive for spontaneous reactions.
In 1923, the Belgian mathematician and physicist Théophile de Donder derived a relation between affinity and the Gibbs free energy of a chemical reaction. Through a series of derivations, de Donder showed that if we consider a mixture of chemical species with the possibility of chemical reaction, it can be proven that the following relation holds:
With the writings of Théophile de Donder as precedent, Ilya Prigogine and Defay in Chemical Thermodynamics (1954) defined chemical affinity in terms of the uncompensated heat of reaction Q' the reaction progress variable or reaction extent ξ; as the ratio of their infinitesimal increments:
This definition is useful for quantifying the factors responsible both for the state of equilibrium systems (where A = 0), and for changes of state of non-equilibrium systems (where A ≠ 0).
History
"Chemical affinity", historically, refers to the "force" that causes chemical reactions.[3] A broad definition, used generally throughout history, is that chemical affinity is that whereby substances enter into or resist decomposition.[4] .
The term affinity has been used figuratively since c. 1600 in discussions of structural relationships in chemistry, philology, etc., and reference to "natural attraction" is from 1616.
The idea of affinity is extremely old. Many attempts have been made at identifying its origins.[4] The majority of such attempts, however, except in a general manner, end in futility since "affinities" lie at the basis of all magic, thereby pre-dating science.[5] Physical chemistry, however, was one of the first branches of science to study and formulate a "theory of affinity". The name affinitas was first used in the sense of chemical relation by German philosopher Albertus Magnus near the year 1250. Later, those as Robert Boyle, John Mayow, Johann Glauber, Isaac Newton, and Georg Stahl put forward ideas on elective affinity in attempts to explain how heat is evolved during combustion reactions.[6]
The modern term chemical affinity is a somewhat modified variation of its eighteenth-century precursor "elective affinity" or elective attractions, a coinage of the Swedish chemist Torbern Olof Bergman from his book De attractionibus electivis (1775). Antoine Lavoisier, in his famed 1789 Traité Élémentaire de Chimie (Elements of Chemistry), refers to Bergmann’s work and discusses the concept of elective affinities or attractions.
Goethe used the concept in his novel Elective Affinities, (1809)
Geoffroy's 1718 affinity table
The first-ever affinity table, which was based on displacement reactions, was published in 1718 by the French chemist Étienne François Geoffroy. Geoffroy's name is best known in connection with these tables of "affinities" (tables des rapports), which were first presented to the French Academy in 1718 and 1720, as shown below:
These were lists, prepared by collating observations on the actions of substances one upon another, showing the varying degrees of affinity exhibited by analogous bodies for different reagents, and they retained their vogue for the rest of the century, until displaced by the profounder conceptions introduced by Claude Berthollet.
See also
- Chemistry
- Chemical reaction
- Chemical bond
- Electronegativity
- Electron affinity
- Étienne François Geoffroy — Geoffroy's 1718 Affinity Table
- Valency
- Affinity chromatography
- Affinity electrophoresis
References
- ^ Chemical Affinity - Britannica 1911
- ^ IUPAC Green Book and Gold Book in .pdf
- ^ Thomas Thomson. (1831). A System of Chemistry, vol. 1. p.31 (chemical affinity is described as an "unknown force"). 7th ed., 2 vols.
- ^ a b Levere, Trevor, H. (1971). Affinity and Matter – Elements of Chemical Philosophy 1800-1865. Gordon and Breach Science Publishers. ISBN 2881245838.
- ^ Malthauf, R. P. (1966). The Origins of Chemistry. Pg. 299. London.
- ^ Partington, J.R. (1937). A Short History of Chemistry. New York: Dover Publications, Inc. ISBN 0-486-65977-1
Notes
- This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
External links
- William Whewell. "Establishment and Development of the Idea of Chemical Affinity". History of Scientific Ideas. 2:15ff.
- Chemical Affinity and Absolute Zero - 1920 Nobel Prize in Chemistry Presentation Speech by Gerard de Geer
- Elements, Principles and the Narrative of Affinity – Essay Review